
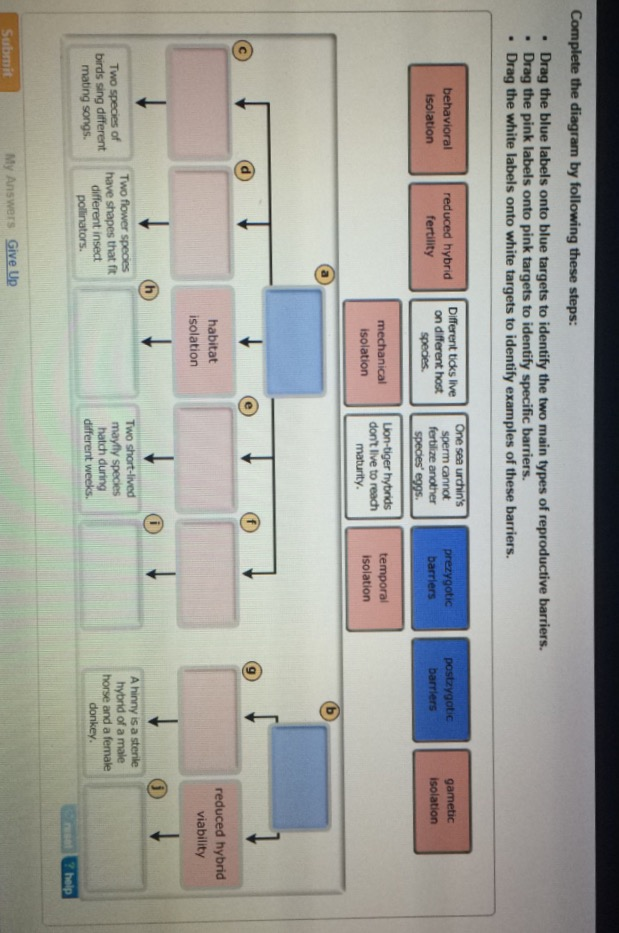

Asparagine (Asn) and glutamine (Gln) are also polar, they carry a polar amide group. This polar group can participate in hydrogen bond formation with another polar group by donating or accepting a proton. For example, serine (Ser), threonine (Thr) and tyrosine (Tyr) are clearly polar since they carry a hydroxyl (-OH) group. When considering polarity, some of the amino acids are straightforward to assign, while in other cases we may encounter disagreements. I hope that at some moment in the future I will complement this compendium by a chapter on metal binding in proteins.
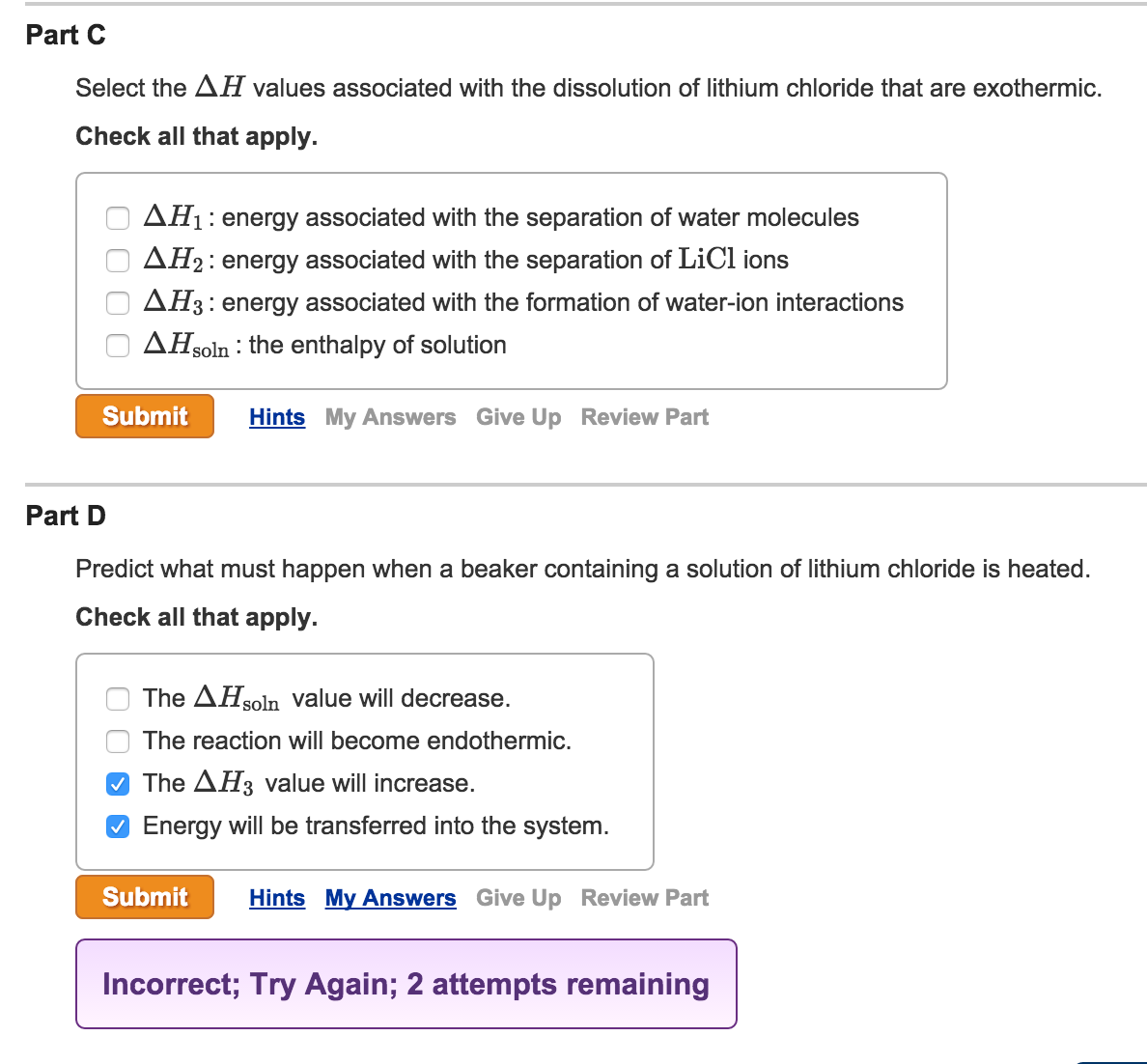
Metalloproteins and metal binding is a fascinating area of structural biology. Binding of metal ions in proteins is another function of the negatively charged carboxylic groups of Asp and Glu. For example, charged amino acids in proteins from thermophilic organisms (organisms that live at elevated temperatures, up to 80-90 C, or even higher) often form an extensive network of salt bridges on the surface of these proteins, contributing to their thermostability and preventing denaturation at high temperatures. The so-called salt bridges, which are formed by the interaction between positively and negatively charged amino acid side chains, have been found to be important for the stabilization of protein three-dimensional structure. There are four of them, two basic amino acids, lysine (Lys) and arginine (Arg) with a positive charge at neutral pH, and two acidic, aspartate (Asp) and glutamate (Glu) carrying a negative charge at neutral pH. It is easy to see which amino acids are charged simply because at neutral pH (around 7) they contain a single charge. For example, based on the propensity of the side chain to be in contact with water, amino acids can be classified as hydrophobic (low propensity to be in contact with water), polar and charged (energetically favorable contacts with water). Each of the 20 most common amino acids has its specific chemical characteristics and its unique role in protein structure and function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
